Limited Print Gaming: Study of Market Leaders
The limited print gaming sector has emerged as a critical bridge between digital distribution and physical game preservation...
Introduction
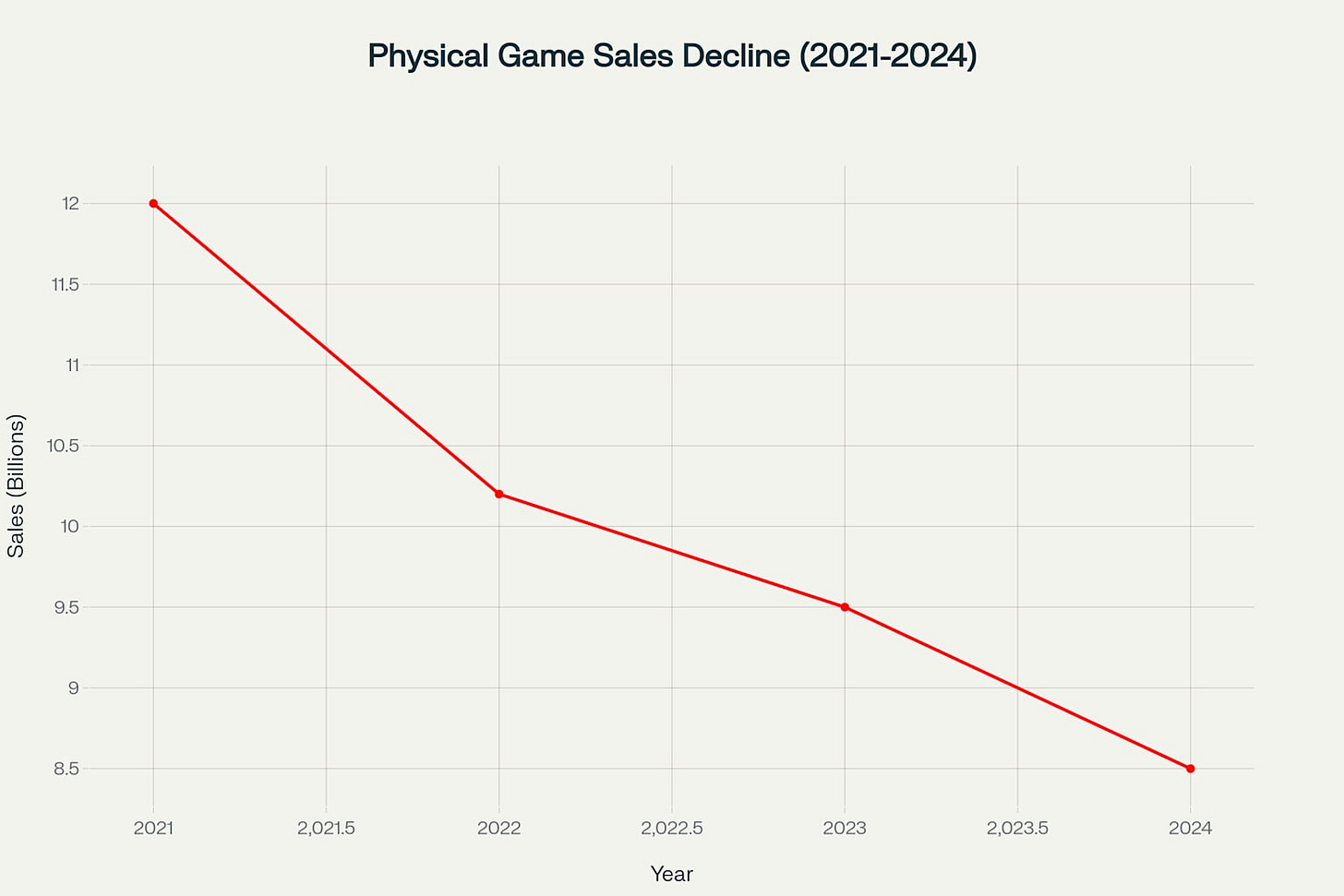
The limited print gaming sector has emerged as a critical bridge between digital distribution and physical game preservation, driven by collector psychology, developer economics, and growing concerns about digital media permanence. This enhanced analysis examines the three dominant market players—Limited Run Games, Special Reserve Games, and Super Rare Games—through the lens of recently revealed internal operations, financial struggles, and controversial business practices that have shaped this specialized industry. The sector operates within a rapidly declining physical media landscape, where global physical game sales dropped nearly 30% from $12 billion in 2021 to $8.5 billion in 2024, creating both challenges and opportunities for specialized publishers.
Limited Run Games: From Near-Bankruptcy to Market Domination
Limited Run Games' origin story reveals a company born from desperation rather than opportunity, fundamentally shaping its business practices and reputation. CEO Josh Fairhurst's journey from $330,000 in personal credit card debt to building a company generating over $150 million in cumulative revenue illustrates both the potential and perils of the limited print gaming model. The company's transformation from Mighty Rabbit Studios, which faced closure with only $10,000 remaining in its bank account, demonstrates how existential threats can drive innovative business models.
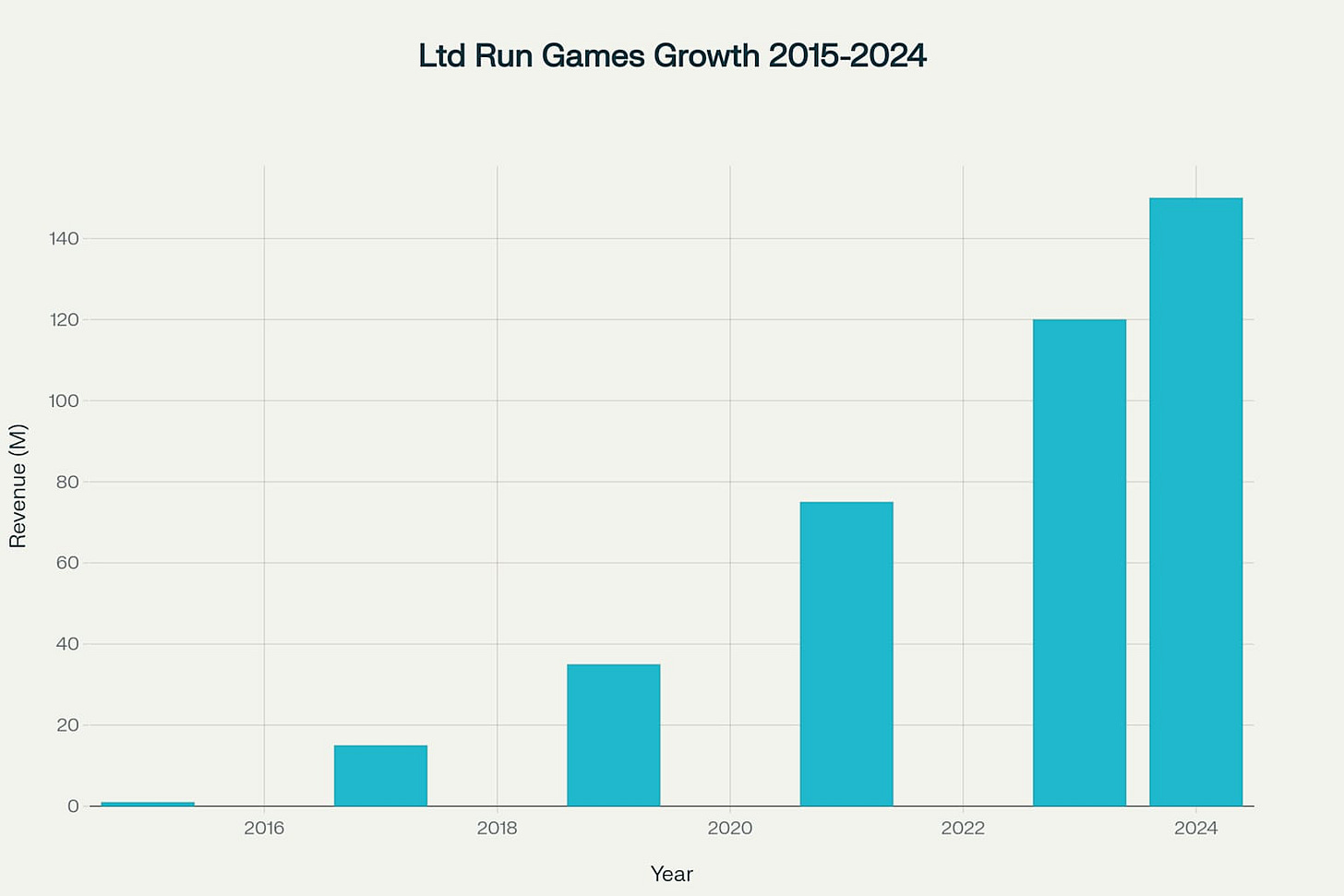
The Economics
The video transcript reveals Limited Run Games' core mission as protecting indie developers from unsustainable digital marketplace pricing, where games often sold for "fractions of a penny" through bundles and sales. However, this preservation narrative masks more complex economic realities where Limited Run Games retains approximately 30% of gross revenue while shouldering manufacturing and distribution risks.
The sector's relationship with indie developers reflects broader power imbalances in the gaming industry. While Limited Run Games positions itself as saving developers from financial ruin, the reality involves careful curation and risk assessment that often excludes smaller or less commercially viable projects.
Market Structure and Competitive Landscape
Revenue Distribution and Market Share Analysis
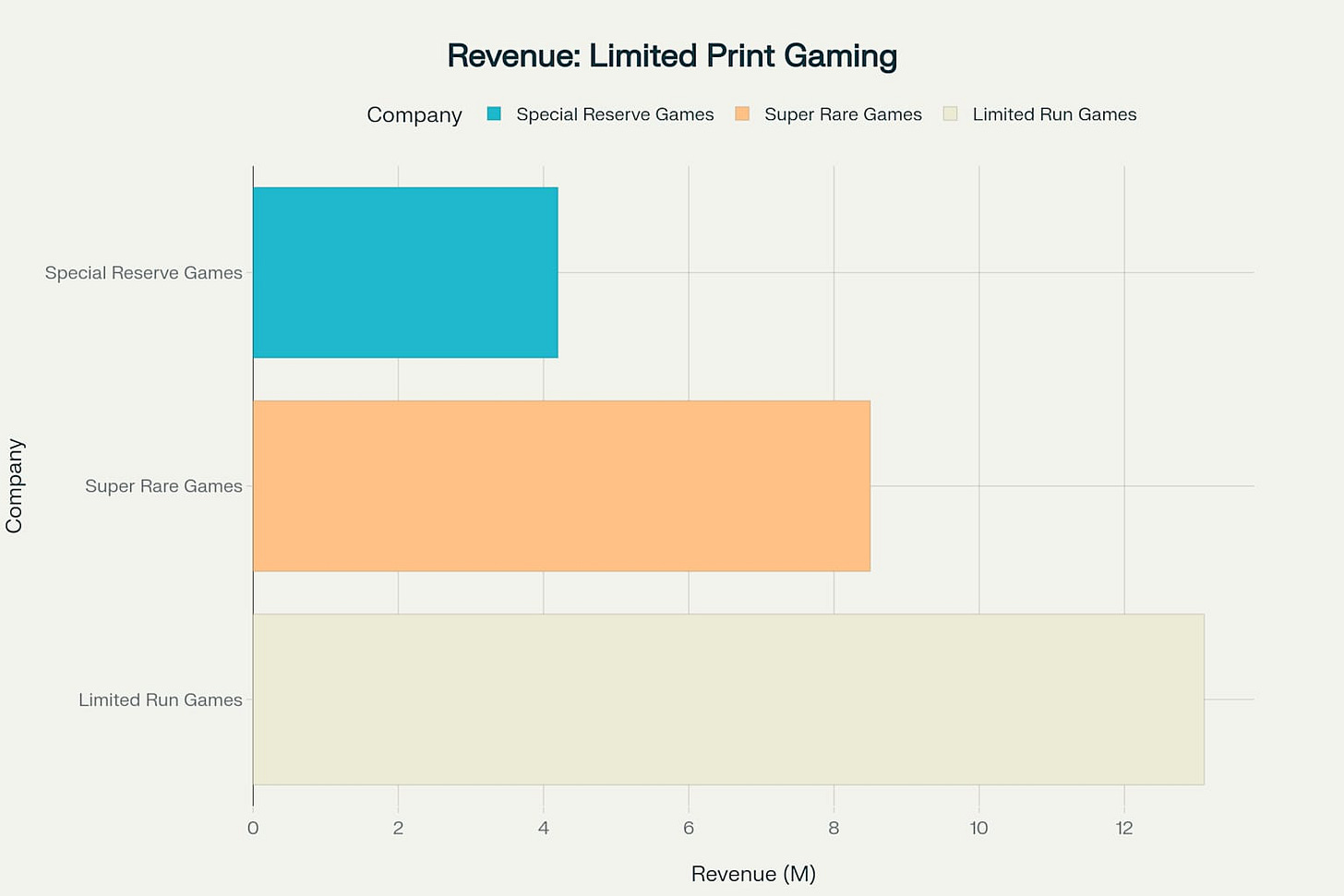
Current market data reveals Limited Run Games' dominant position with $13.1 million in annual revenue, compared to Super Rare Games' $8.5 million and Special Reserve Games' $4.2 million. This revenue distribution reflects different strategic approaches to market positioning and target demographics. Limited Run Games' strategy of volume production with average print runs of 8,000 units contrasts sharply with Super Rare Games' focus on exclusivity with 4,000-unit runs and Special Reserve Games' premium positioning with 2,500-unit average runs.
The competitive dynamics reveal how each company has carved distinct niches within the broader limited print gaming ecosystem. Super Rare Games' focus on Nintendo Switch releases and fixed production quantities creates stronger collector appeal than demand-based manufacturing systems. Special Reserve Games' emphasis on premium packaging and close publisher relationships, particularly with Devolver Digital, targets high-value collectors willing to pay premium prices for exceptional presentation.
Platform Specialization and Geographic Distribution
The three companies demonstrate different approaches to platform specialization and market coverage. Super Rare Games' initial focus on Nintendo Switch reflected the platform's continued support for physical media and strong collector community, with the company releasing over 90 titles before expanding to PlayStation platforms in 2023. Limited Run Games' multi-platform approach covers Nintendo Switch, PlayStation, Xbox, and PC, reflecting its volume-based business model and broader market appeal.
Geographic distribution patterns reveal how limited print gaming companies navigate international markets and shipping complexities. Limited Run Games' expansion beyond North America required significant logistical investment and regulatory compliance, while Super Rare Games' London base provided natural access to European markets. Special Reserve Games' more limited geographic reach reflects its boutique positioning and premium pricing strategy.
The Broader Gaming Collectibles Ecosystem
Market Context and Valuation
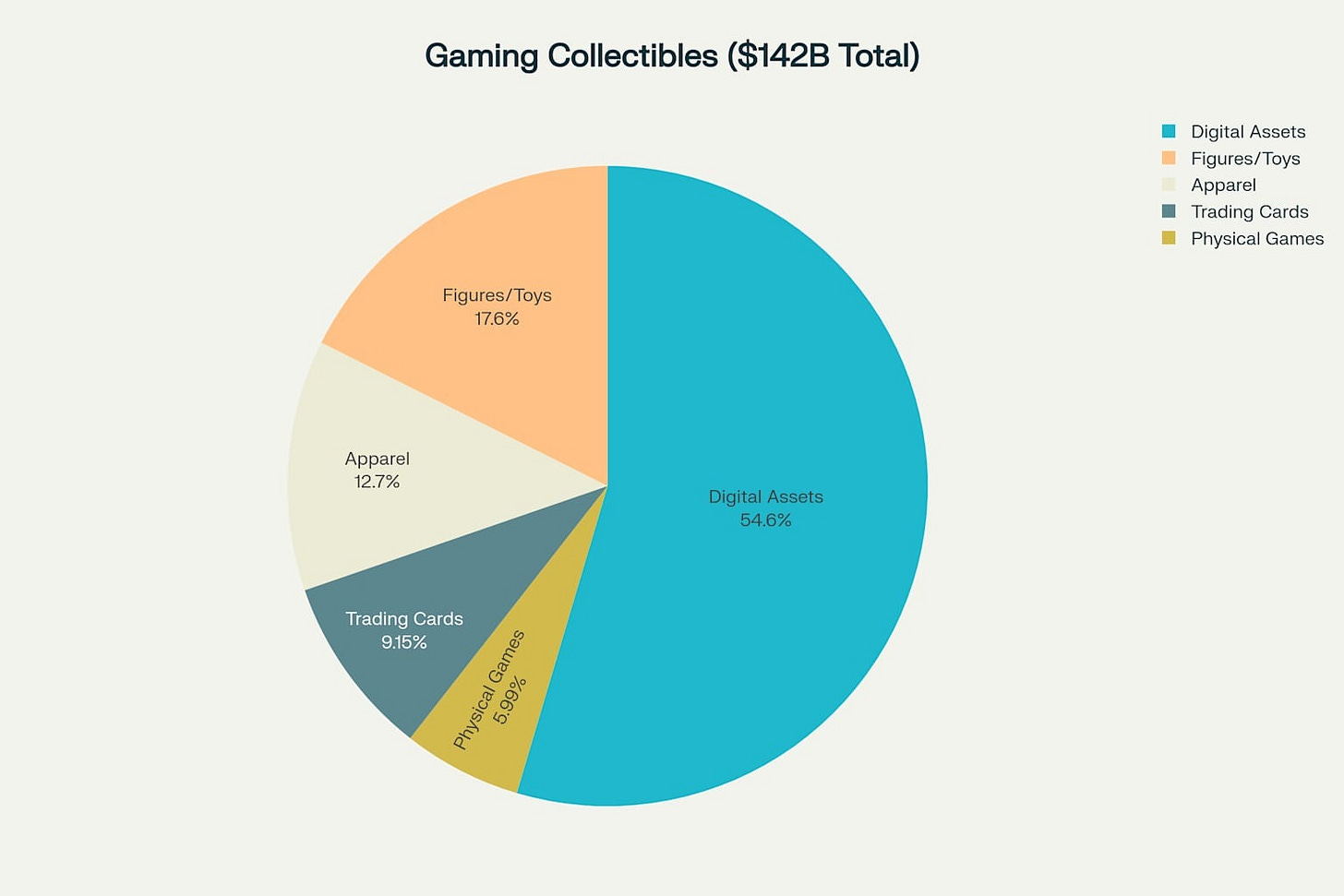
Limited print gaming operates within a $142 billion gaming collectibles market dominated by digital assets, which account for $77.5 billion or 55% of total value. Physical games represent only $8.5 billion or 6% of this broader market, highlighting both the niche nature of limited print gaming and its potential for growth within established collector behaviors. The gaming merchandise market's projected 20% compound annual growth rate through 2032 provides favorable conditions for specialized physical gaming products.
The collectibles market structure reveals how limited print gaming companies must compete not just with each other but with broader entertainment collectibles. Trading cards worth $13 billion, figures and toys worth $25 billion, and gaming apparel worth $18 billion all target similar collector demographics and discretionary spending. This competitive context explains why limited print gaming companies increasingly emphasize premium packaging, exclusive artwork, and collectible extras beyond the games themselves.
Consumer Psychology and Purchasing Motivations
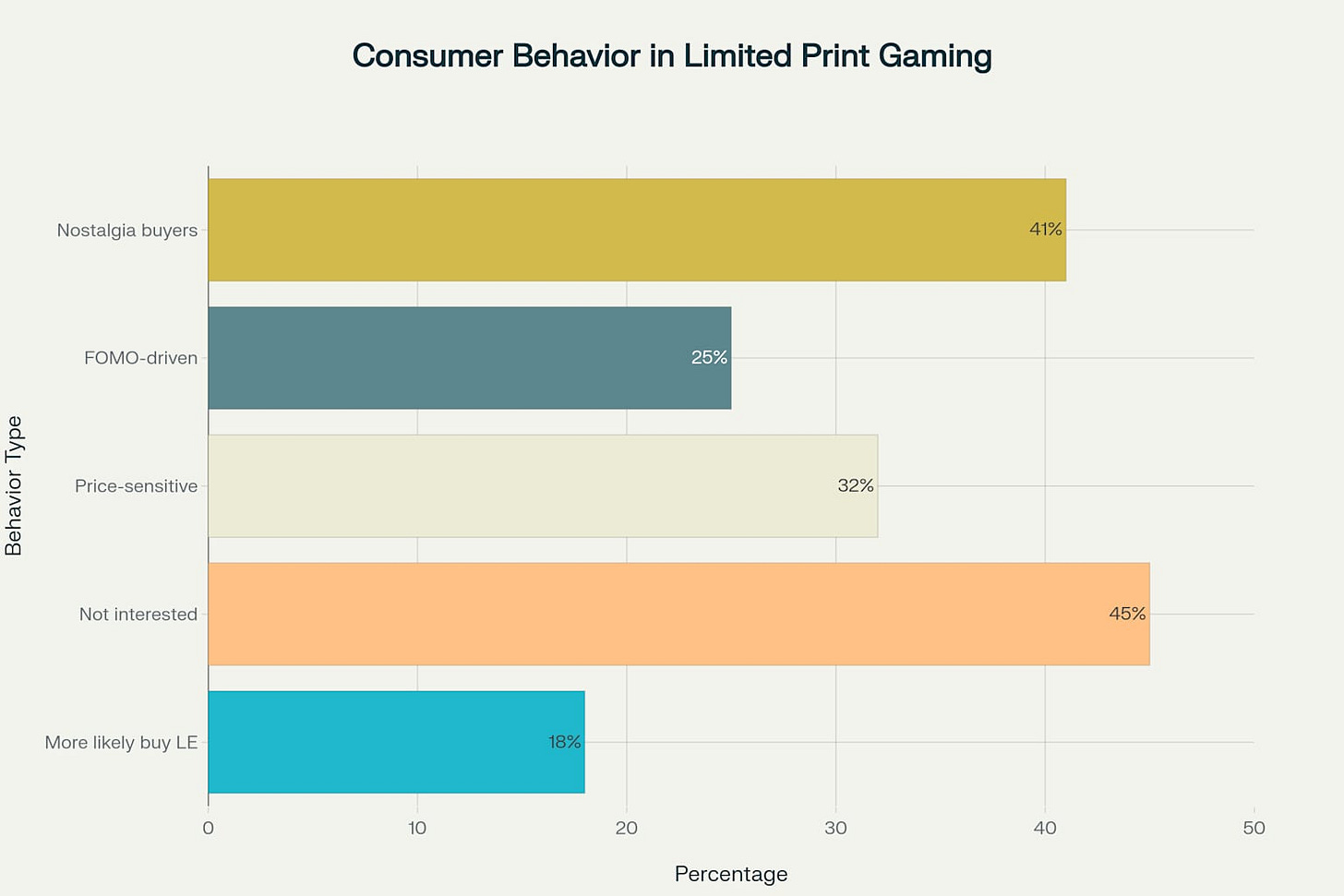
Analysis of consumer behavior within the limited print gaming market reveals complex psychological drivers that extend beyond simple game ownership. Research indicates that 41% of consumers are motivated by nostalgia, while 25% are driven by fear of missing out (FOMO) psychology that enables rapid sell-outs. However, 45% of respondents express no interest in limited editions, highlighting the market's inherent constraints and the importance of precise targeting.
The psychological appeal of physical ownership in an increasingly digital world creates unique marketing opportunities and challenges. Collectors often purchase games they never intend to play, viewing them as cultural artifacts worthy of preservation and display. This behavior supports higher price points and premium packaging but also creates ethical questions about the relationship between preservation missions and commercial exploitation.
Future Outlook and Strategic Implications
Digital Transformation Challenges
The limited print gaming sector faces existential challenges as the broader industry accelerates toward digital-only distribution. Nintendo's announcement that digital Switch 2 games will be priced lower than physical versions in key markets represents an unprecedented threat to physical media collecting. This pricing strategy, combined with the introduction of game-key cards that provide digital codes in physical packaging, suggests even Nintendo is hedging its commitment to traditional physical media.
The decline of physical retail infrastructure compounds these challenges, with major retailers reducing floor space dedicated to physical games. While specialty gaming stores may benefit from reduced competition, the overall ecosystem supporting physical game distribution continues to contract. Limited print gaming companies must navigate this declining infrastructure while maintaining the collector appeal that drives their business models.
Consolidation and Market Evolution
The acquisition of Limited Run Games by Embracer Group signals broader industry consolidation that may reshape competitive dynamics. Embracer's ownership provides access to extensive intellectual property libraries through subsidiaries like Gearbox Entertainment, potentially enabling Limited Run Games to produce physical versions of major franchises previously unavailable in limited print formats. However, this corporate integration may also constrain the entrepreneurial agility that initially enabled rapid market adaptation.
Super Rare Games' expansion into original publishing through Super Rare Originals represents strategic vertical integration that could provide competitive advantages. By funding original game development rather than simply licensing existing titles, the company creates exclusive content that cannot be replicated by competitors. This strategy requires significantly higher capital investment but offers potentially greater long-term returns and market differentiation.
Conclusions and Strategic Recommendations
The limited print gaming market occupies a unique position at the intersection of digital distribution, physical preservation, and collector psychology. While the sector has demonstrated remarkable growth from Limited Run Games' humble origins to a multi-hundred-million-dollar industry, recent controversies reveal fundamental tensions between commercial success and the preservation mission that originally justified these companies' existence.
The evidence suggests that limited print gaming will survive the ongoing digital transformation, but success will require addressing current operational failures and ethical lapses. Companies that prioritize transparency, quality control, and genuine customer service while maintaining collector appeal will likely thrive, while those that exploit customer trust for short-term profits risk regulatory intervention and market rejection.
The sector's future depends on resolving contradictions between preservation rhetoric and commercial reality. Authentic commitment to game preservation requires long-term thinking about media longevity, accurate representation of product limitations, and honest communication about production practices. Companies that can balance these ethical imperatives with commercial viability will shape the industry's evolution and cultural impact for decades to come.